Phần này là bổ xung cho việc ngày xưa không được học toán bằng tiếng Anh nên nhiều thuật ngữ tiếng Anh liên quan đến matrix không biết (mặc dù được học rồi :)
1.
Identity matrix (unit matrix - ma trận đơn vị)
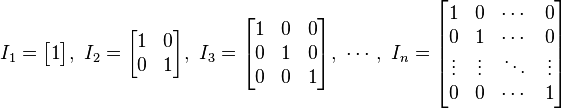
2. Diagonal matrix (ma trận đường chéo)
3. Trace (linear algebra)
In linear algebra, a Trace of an n-by-n square matrix
A is defined to be sum of the elements on the main diagonal of matrix

4. Eigenvalue, Eigenvector and Eigenspace
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eigenvalue,_eigenvector_and_eigenspace
5. Eigenvalue relationships
If
A is a square
n-by-
n matrix with
real or
complex entries and if λ
1,...,λ
n are the (complex and distinct)
eigenvalues of
A (listed according to their
algebraic multiplicities), then

This follows from the fact that
A is always similar to its
Jordan form, an upper
triangular matrix having λ
1,...,λ
n on the main diagonal. In contrast, the
determinant of
A is the
product of its eigenvalues; i.e.,

More generally,





Không có nhận xét nào:
Đăng nhận xét