Laplace operator được định nghĩa như sau:
The Laplace operator is a second order differential operator in the n-dimensional Euclidean space, defined as the divergence (∇·) of the gradient (∇ƒ). Thus if ƒ is a twice-differentiable real-valued function, then the Laplacian of ƒ is defined by
 (1)
(1)
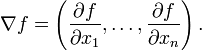
Lại có công thức của devergence như sau:
The divergence of a vector field can be defined in any number of dimensions. If
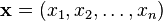 and
and  , define
, define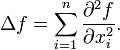 (2)
(2)Chủ yếu chúng ta quan tâm đến công thức của toán tử laplace cho 2 chiều
Two dimensions
The Laplace operator in two dimensions is given byIn polar coordinates,




Không có nhận xét nào:
Đăng nhận xét